
- Home
- About Us
- Sustainability
- Investors
- News
- People & Culture
-
Regions

Accurate reporting of scope 3 emissions has become an essential component of MTN Nigeria’s climate strategy. Beyond regulatory compliance with emerging standards such as IFRS S2, robust data on value chain emissions supports the company’s wider sustainability ambitions. Effective tracking of Scope 3 emissions enables MTN Nigeria to design targeted reduction strategies, enhance operational efficiency, and promote supplier accountability. It also reinforces climate disclosures, strengthens investor confidence, and positions the business as a responsible and forward-thinking leader in the Nigerian market.
As part of its commitment to Nigeria’s Energy Transition Plan (ETP) and in alignment with MTN Group’s ambition to achieve Net Zero emissions by 2040, MTN Nigeria has prioritised the development of a structured, transparent approach to managing Scope 3 emissions. These emissions represent the most extensive and complex share of the company’s carbon footprint, spanning indirect sources such as upstream supply chain activities, product use, and end-of-life treatment of equipment.
The programme is anchored in the adoption of IFRS Sustainability Reporting Standards, which guide MTN Nigeria’s disclosure framework and support the integration of value chain emissions data into its broader environmental performance strategy. It structured around the following key components:
Scope 3 emissions: A clear understanding of indirect emissions, encompassing those from the supply chain, product use and end-of-life treatment of equipment.
Data collection process: Implementation of a rigorous data collection process, facilitated by external carbon specialists and MTN’s Sustainability team. This process includes onboarding of Single Points of Contact (SPOCs), in-depth sessions on Scope 3 categories and the use of standardised data templates for consistent reporting.
Stakeholder engagement: Proactive engagement with internal teams and external suppliers through workshops, onboarding sessions and ongoing support to ensure accurate and transparent data reporting.
Strategic alignment: Alignment with the MTN Group’s Project Zero strategy, which emphasises collaborative efforts with suppliers to achieve Net Zero emissions by 2040.
The initiative has yielded significant achievements:
Comprehensive data collection: MTN Nigeria implemented a bottom-up approach to gathering detailed data across all relevant Scope 3 categories directly from sources within the value chain, marking a first.
Enhanced data quality: Improvement in data accuracy and reliability using standardised templates, periodic reviews and close collaboration with ERM.
Strengthened stakeholder collaboration: Cultivation of stakeholder ownership through SPOC onboarding sessions and workshops, leading to increased transparency and engagement across departments and suppliers.
Strategic alignment: Advancement of Nigeria’s ETP goals and reinforcement of MTN’s emissions tracking framework for long-term sustainability planning.
MTN Nigeria will continue to refine its Scope 3 reporting approach, focusing on improving methodologies and expanding collaboration with supply chain partners. As data maturity increases, so too will the ability to identify high-impact reduction opportunities and to support the broader ambitions of MTN Group’s Net Zero pathway.
Ongoing stakeholder engagement, capacity building, and process optimisation will remain central to this effort. As the initiative evolves, it will play an increasingly important role in embedding climate accountability across MTN’s operations and in shaping sector-wide progress toward sustainable value chains.

Reliable energy access remains a persistent barrier to digital connectivity in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA). Less than 1% of households have access to fixed broadband, and many mobile operators face frequent power outages, limited grid access, and rising operational costs due to fuel dependence. The region’s heavy reliance on diesel generators, exacerbated by rising fuel prices and frequent theft of equipment, makes mobile network operation challenging.
These challenges undermine the delivery of essential mobile services and hinder broader progress towards the region’s sustainable development goals. Strengthening energy access for mobile networks has become a key priority in ensuring connectivity remains stable and inclusive.
In response to these constraints, GSMA partnered with mobile operators, regulators, and policymakers across the region to explore the energy-related obstacles facing digital infrastructure. The resulting report, Energy Challenges for Mobile Networks in sub-Saharan Africa, provides an in-depth look at how energy insecurity affects the performance and expansion of mobile networks.
Angela Wamola, Head of sub-Saharan Africa at GSMA, emphasised the essential role of energy in enabling digital transformation across the continent. Recognising that mobile networks are a backbone of progress in SSA, GSMA has been at the forefront of advocating for innovative, low-carbon energy solutions to help operators overcome power-related barriers and ensure greater service reliability.
The research and collaborative efforts have led to some positive outcomes in the region:
Deployment of renewable solutions: Mobile operators have increasingly turned to solar energy and battery storage solutions to maintain connectivity. In South Africa, operators have partnered with Eskom and the government to access renewable energy from independent power producers, improving reliability and reducing energy costs.
Improved policy environment: Countries like Kenya and Uganda have seen success in expanding access to energy, with Kenya now generating over 90% of its electricity from renewable sources. Namibia has positioned itself as a leader in solar energy development through effective policy reforms, attracting private investment.
Collaboration and cost-effective solutions: Mobile operators in South Africa have worked together, allowing them to jointly procure backup power and security. This shared approach has helped reduce costs and improve network stability.
While significant progress has been made, energy insecurity remains a challenge across much of SSA. The GSMA continues to advocate for policy environments that support private sector investment in renewable energy and the expansion of mini-grids. These shifts will be critical to ensuring a stable, sustainable energy supply for mobile networks across the region.
Ongoing collaboration among operators, government stakeholders, and energy providers will be key to unlocking further progress. With the right frameworks in place, energy reliability can become a catalyst for advancing both digital inclusion and climate resilience across sub-Saharan Africa.

Extreme weather events continue to disrupt lives and livelihoods across Africa. With agriculture-dependent populations especially vulnerable, there is a growing need for accessible and timely information to help people prepare for climate-related disruptions. As part of its approach to climate resilience, MTN Group is advancing digital solutions that support early warning and informed decision-making.
This work is underpinned by a strategic alliance between MTN, Tomorrow.io, and Microsoft to develop a continent-wide early warning system. The initiative brings together climate intelligence, cloud computing, and mobile connectivity to deliver localised weather alerts directly to people’s mobile phones.
To address the growing risk of extreme weather, MTN Group is working with Tomorrow.io and Microsoft to build a digital early warning system capable of reaching more than 300 million people. The solution integrates Tomorrow.io’s hyperlocal weather engine with Microsoft’s Azure cloud infrastructure and MTN’s network presence across Africa to deliver actionable alerts where they are needed most.
In Nigeria, this partnership has taken a step forward through a collaboration between MTN Nigeria, the Nigerian Meteorological Agency (NiMet), and Tomorrow.io. In January 2024, the partners formalised their cooperation through a Memorandum of Understanding, launching the Digital Climate Advisory Services (DCAS) platform. This initiative focuses on providing smallholder farmers with location-specific, mobile-based weather advisories that support better planning around planting, irrigation, and harvesting.
The platform combines NiMet’s meteorological expertise, Tomorrow.io’s data modelling capabilities, and MTN’s telecommunications infrastructure. Together, these elements ensure that farmers receive timely and relevant weather insights that can help reduce climate-related risks and improve agricultural productivity. The collaboration also aligns with the United Nations’ “Early Warnings for All” initiative, contributing to broader global efforts to improve disaster preparedness and community resilience.
Under the terms of the MoU, the three parties will collaborate to develop, deploy, and test the DCAS platform. The system will provide weather-based advisories to farmers through mobile notifications, enabling them to make informed decisions about planting, irrigation and harvesting. By delivering hyperlocalised weather forecasts and actionable insights, the DCAS system will help farmers adapt to climate variability, reduce crop losses, and improve yields.
This partnership reflects a shared commitment to building climate resilience through technology and collaboration. As the DCAS system scales, it has the potential to benefit millions of farmers across Nigeria and beyond. By enabling timely access to weather intelligence, MTN, NiMet, and Tomorrow.io are working together to support more adaptive, informed, and sustainable agriculture.

As climate-related risks intensify, a new generation of climate entrepreneurs is emerging across Africa with solutions that address environmental challenges while creating local economic opportunity. Supporting these climate-focused ventures is an environmentally responsible step that also strengthens local economies, enhances resilience, and builds leadership capacity among young people.
Africa’s demographic profile and environmental context present a unique opportunity. Youth-led innovation can play a catalytic role in tackling issues such as water scarcity, food insecurity, and land degradation, while also advancing inclusive growth and community development. Enabling these ventures contributes to MTN’s broader ambition to foster sustainable, local solutions that reflect the realities and priorities of the continent.
The Africa PachiPanda Challenge was designed to meet two core objectives: advancing environmentally focused innovation and contributing to local socioeconomic development. Building on the momentum of MTN Zambia’s Innovation Challenge in 2022 and 2023, the initiative was expanded into a multi-country programme in 2024, in partnership with the World Wildlife Fund (WWF).
In 2024, the competition was rolled out by MTN Nigeria, MTN South Africa, and MTN Zambia, aligned with our Group-wide sustainability strategy and commitment to climate entrepreneurship.
The programme received 2,298 applications, reflecting strong interest and readiness across markets. Finalists were selected to participate in a pitch and development programme, with 30 participants supported through tailored training and capacity-building.
Through scaling and replication, the Africa PachiPanda Programme has been implemented across multiple MTN markets to maximise its positive impact. The 2024 challenge received 2 298 applications, with 30 finalists supported through a structured pitch and development programme. The initiative surfaced a pipeline of early-stage ventures, many of which address highly localised environmental risks. The selected entrepreneurs demonstrated practical, solutions-oriented thinking and a clear commitment to sustainability, reflecting the growing depth and potential of Africa’s climate innovation landscape.
The Challenge will expand to include Uganda, , as part of MTN’s goal to support a broader ecosystem of green entrepreneurs. The programme aims to contribute to job creation, innovation in the green economy, and community-level resilience by enabling climate-smart ventures to grow and scale.
As we continue to invest in youth-led climate entrepreneurship, we remain committed to supporting solutions that are both environmentally impactful and economically viable, helping drive a more sustainable and inclusive future across our footprint.
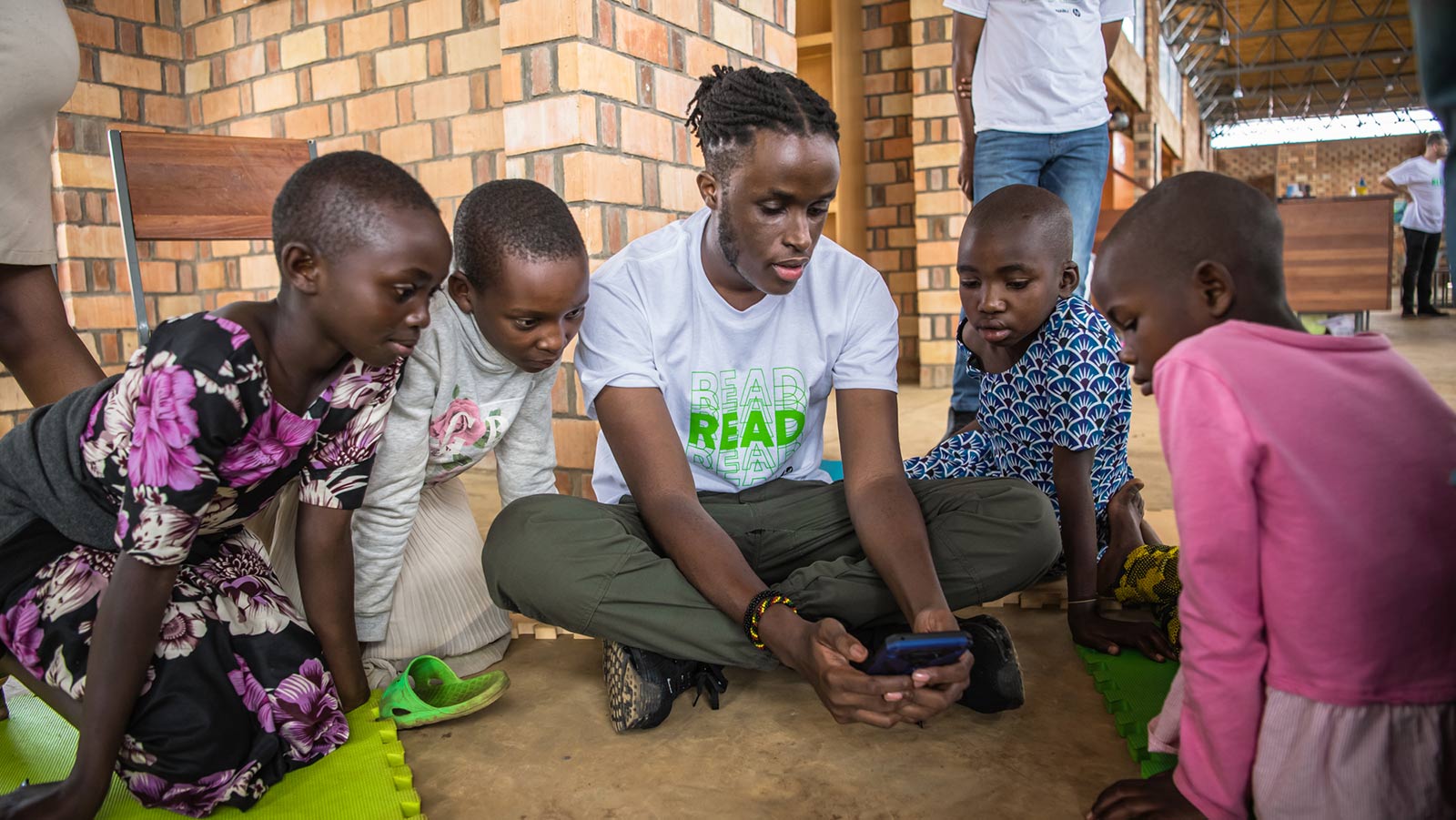

As part of MTN’s broader commitment to social responsibility and environmental sustainability, Project Infinity reflects a practical application of circular economy principles. One of the pilot initiatives under this programme focused on improving educational access and literacy in Rwanda, while promoting device reuse to reduce waste and avoid emissions.
The literacy pilot programme illustrates how technology and collaboration can be leveraged to address systemic challenges like illiteracy. MTN South Africa contributed 894 unused smartphones to the initiative, repurposed through circularity partner GSM Systems. In partnership with Nabu, the Ministry of Education in Rwanda, and local implementation partners, these devices were delivered to 76 schools across seven districts.
Each device was pre-installed with the Nabu reading app — a free digital platform designed to build foundational literacy for children aged 5 to 15. The app features a library of culturally relevant stories in local languages and supports a gradual transition to English as learners progress, expanding their access to broader educational content. This approach promotes early reading engagement while opening pathways to further learning.
To ensure effective use, 641 teachers received training on how to incorporate the devices and app into their classrooms. Over a five-month period, the programme recorded a 276% increase in reading time and a 13% increase in book completion rates, demonstrating improved learner engagement and content retention.
Beyond educational outcomes, the initiative also reflects MTN’s commitment to responsible consumption and circular economy practices. By redistributing idle devices, the programme avoided the need for new device production, contributing to emissions avoidance of 51 tCO₂e. This is equivalent to:
The Rwanda pilot programme has shown promising results, and we are excited about potential partnership opportunities for expansion. MTN is exploring opportunities to expand the initiative through new partnerships, with growing interest from corporates, NGOs, and educational stakeholders.
We welcome collaboration to scale this model to additional communities. By working together, we can help close educational gaps, extend the life of existing technology, and support emission reductions in line with MTN’s broader Net Zero ambition.

As a key infrastructure partner to MTN, American Tower Corporation (ATC) plays an important role in supporting the Group’s journey toward Net Zero. Managing a significant portion of MTN’s tower infrastructure in South Africa, Nigeria, Uganda and Ghana, ATC is actively working to align its operations with MTN’s emissions reduction objectives.
ATC’s decarbonisation strategy is guided by a future‑focused, science‑based approach, focusing on three strategic pillars: enhancing energy efficiency, expanding renewable energy integration and advancing energy storage capabilities.
Energy efficiency: ATC continues to improve energy performance by deploying advanced energy management systems and retrofitting sites with more efficient technologies – particularly in high‑usage markets, helping reduce site-level power consumption and emissions.
Renewable energy: The business is accelerating the transition to renewable energy by deploying on‑site solar power solutions, helping to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and enhance energy resilience across multiple markets.
Energy storage: ATC’s investment in cutting‑edge energy storage solutions, such as lithium‑ion batteries, supports more stable and reliable renewable energy use, particularly in areas with irregular grid access or fuel supply constraints.
These focused efforts reflect a shared commitment to reducing environmental impact and building greater operational resilience across the telecoms value chain.
The ongoing collaboration between MTN and ATC has already delivered measurable outcomes:
ATC remains committed to supporting MTN’s Net Zero ambition through ongoing collaboration, innovation, and strategic investment. By continuing to align with global energy trends and MTN’s climate roadmap, the partnership aims to strengthen environmental performance while contributing to a more resilient, low-carbon network.
This joint approach reflects a broader commitment to climate responsibility and the role infrastructure providers play in advancing sustainable digital ecosystems. .

MTN Nigeria’s 2024 focus under Project Zero centred on improving energy efficiency at high-consumption sites across its network. Led by the Power Management team, the flagship initiative involved replacing 86 outdated HVAC units with high-efficiency cooling systems across data centres, switch centres, and BTS locations.
These upgrades were introduced to support the network’s growing energy demands while reducing operational strain. The new systems significantly lowered power consumption, improved diesel efficiency, and contributed to MTN Nigeria’s broader emissions reduction targets under the Reduce pillar of MTN Group’s Net Zero strategy.
Nigeria’s power sector is marked by persistent grid instability, with 12 national grid collapses reported in 2024, and continued dependence on diesel generators. These conditions drive high operational costs, increase carbon emissions, and expose infrastructure to performance risks.
With rising energy prices and expanding network coverage, MTN Nigeria identified an urgent need to address inefficiencies across its energy-intensive facilities. By modernising HVAC infrastructure, the business has made measurable progress in reducing fuel use, improving power stability, and lowering emissions.
In 2024, MTN Nigeria achieved an 11% reduction in Scope 1 and 2 emissions against a target of 12.5% amounting to a total emissions reduction of 12 526tCO2e. This case study illustrates the successful application of the Reduce pillar of MTN’s Net Zero philosophy.
A 2% reduction in base-year emissions, decreasing from 3 784tCO2e before implementation to 2 314tCO2e afterwards.
NGN508 792 620 saved over two quarters, with annual savings still being calculated.
Lower operational energy demand and reducing reliance on diesel consumption.
MTN Nigeria’s investment in energy efficiency marks a critical step in its Net Zero journey. Future plans include scaling renewable deployments and expanding efficiency upgrades, ensuring long-term sustainability and cost savings while reinforcing MTN’s leadership in green energy transitions.
MTN Ghana continues to advance its emissions reduction efforts through the targeted deployment of renewable energy and improvements in infrastructure efficiency. Under Project Zero, the business is transitioning high energy-consuming facilities to cleaner power sources while reducing operational energy use through modernised cooling systems and energy-efficient lighting upgrades.
The 2024 programme included interventions at three data/switch centres, the MTN House facility, and 39 BTS sites. Solar power systems were installed at sites in Accra, Kumasi and other locations, bringing the total installed capacity to 2.4 MW. As a result, 64% of switch/data centre energy and 54% of BTS site energy now come from green sources.
To further improve efficiency, MTN Ghana implemented its Cooling Unit Modernisation project, replacing 84 conventional cooling systems with variable-speed compressor units, significantly reducing power consumption at critical facilities.
Ghana’s energy sector faces high electricity costs, rolling blackouts (“dumsor”) owing to grid instability and heavily relies on fossil fuels as an energy source. These conditions contribute to increased emissions and operational volatility for businesses with large-scale infrastructure needs.
To reduce exposure to these risks, MTN Ghana prioritised energy transformation through a combination of solar integration and infrastructure upgrades, applying the Reduce pillar of MTN Group’s Net Zero strategy. In 2024, the business achieved an 11% reduction in Scope 1 and 2 emissions against a target of 12.5%. The actual emissions reduction achieved was 4 339tCO2e.
15.6% decrease in emissions. In 2023 an emissions reduction of 2 136tCO2e was achieved and in 2024 an emissions reduction value of 3 325tCO2e was achieved.
US$0.46 million in 2024 with a cumulative savings of US$0.80 million since 2022.
3.1MWh saved from grid power. 12% to 16% reduction in cooling power
consumption. 265 000 litres of diesel saved.
MTN Ghana aims to further optimise energy efficiency and scale its green initiatives. By 2027, the full implementation of its solar energy and cooling system modernisation projects is expected to enhance operational resilience, reduce environmental impact and drive sustainable cost efficiencies across its network.

MTN Cameroon’s 2024 activities under Project Zero focus on lowering carbon emissions by integrating renewable energy solutions and enhancing energy efficiency across its network operations. Interventions included the deployment of on-grid solar systems, hybrid generator/battery solutions, and air conditioning upgrades to optimise energy consumption and emission reduction across 44 BTS sites.
A key initiative was the implementation of an on-grid solar system at the Garoua Switch – designed for daytime self-consumption, feeding solar power directly into the building’s energy system without exporting to the national grid. This shift supports greater energy stability and reduces dependence on high-carbon power sources.
Cameroon faces increasing energy costs and growing demands, with MTN Cameroon having to depend on unstable conventional power sources. The inefficiency of traditional diesel generators and grid electricity poses financial and environmental risks, impacting operational sustainability. To address these challenges, MTN Cameroon needed a reliable, cost-effective and cleaner energy solution to optimise power consumption and reduce emissions, in support of its Net Zero commitments. In 2024, MTN Cameroon achieved a 5.8% reduction in Scope 1 and 2 emissions against a target of 12.5%. The actual emissions reduction achieved was 644tCO2e. This case study illustrates the successful application of the Substitute pillar of MTN’s Net Zero philosophy.
The Garoua Switch solar project has saved 72.12MWh of energy, equivalent to reducing 19.47tCO2e.
The project resulted in savings of approximately US$11 279.43.
The project improved power reliability, which supports uninterrupted operations, ensuring consistent quality.
MTN Cameroon’s commitment to sustainability is driving greater reliance on renewable energy and energy efficient technologies. By expanding solar solutions and scaling hybrid power projects, MTN is ensuring a resilient, low-carbon network, which is aligned with its Net Zero goals.

In 2024, as part of its Project Zero strategy, MTN Uganda focused on improving energy efficiency to reduce emissions, strengthen infrastructure reliability, and improve operational resilience. Key interventions included the installation of lithium-ion batteries, generator replacements, rectifier upgrades, and the deployment of Automatic Voltage Stabiliser (AVS) at two regional data centres.
The AVS initiative was implemented to address ongoing voltage fluctuations that had contributed to excessive generator use and power inefficiencies. Since the installation, voltage levels have stabilised, protecting sensitive equipment from potential damage and significantly reducing generator run hours.
Uganda faces growing energy demand and high carbon emissions due to its reliance on diesel-powered generators for backup power. Frequent voltage fluctuations not only increase fuel consumption and operational costs, but also lead to premature equipment failure and inefficiencies. To address these challenges, MTN Uganda needed a solution to stabilise power supply, reduce generator dependence and improve energy efficiency, ultimately lowering carbon emissions and enhancing network resilience. In 2024, MTN Uganda achieved a 58.40% reduction in Scope 1 and 2 emissions against a target of 12.5%. The actual emissions reduction achieved was 6 935tCO2e. This case study illustrates the successful application of the Reduce pillar of MTN’s Net Zero philosophy.
The project reduced 3.11tCO2 emissions in 2024.
Achieved monthly cost saving of US$289.32, with projected annual savings of US$3 471.78.
This initiative focused on power stability, including voltage drops, by ensuring that equipment operates within the required voltage range.
MTN Uganda remains committed to advancing its tailored emissions reduction plan and strengthening its infrastructure to support long-term sustainability goals. The business will continue to implement efficiency-focused upgrades, optimise power use, and invest in scalable technologies to support its Net Zero ambition.